EFV: Bank and Japanese Value ETF Heavy (BATS:EFV)

Matteo Colombo/DigitalVision via Getty Images
This series of articles aims to evaluate exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in relation to their past performance and portfolio metrics. Reviews with updated data will be published as needed.
EFV Strategy
iShares MSCI EAFE Value ETF (Bat: EFV) started It began investment operations on August 1, 2005 and tracks the MSCI EAFE Value Index. It has 474 holdings, a 30-day SEC yield of 3.41%, and an expense ratio of 0.34%. Distributions are paid semiannually. As described in the prospectus iShares,
The underlying index targets a free-float market cap coverage of approximately 50% of the MSCI EAFE Index and is comprised of securities classified by MSCI as most representative of the investment value style. Securities classified in this style generally tend to have higher value characteristics (i.e., higher price-to-book value, price-to-value 12-month forward earnings, and dividend yield).(…) Each security in the MSCI EAFE Index has a specific Evaluated according to criteria. The Value Factor and Growth Factor are used to calculate the Value Score and Growth Score. MSCI uses these two scores to determine the extent to which each security is allocated to the value or growth style.
The process for creating overlapping value and growth sets from parent indices is similar to S&P Dow Jones Indices’ value index definition. However, some metrics are different. Portfolio turnover for the most recent fiscal year was 22%. This article uses the top index represented by the iShares MSCI EAFE ETF (EFA) as the benchmark.
EFV Portfolio
Europe is the heaviest region, followed by Japan, the UK, and France. Compared to the parent indices, EFV is slightly overvalued in the UK, Germany, Italy, Spain, Finland and Norway. We are mainly underweight the Netherlands, Sweden and Denmark. With an asset weighting of 1.84%, Hong Kong has low direct exposure to geopolitical and regulatory risks related to China.
Geographic Allocation as % of Asset Value (Chart: Author: Data: iShares)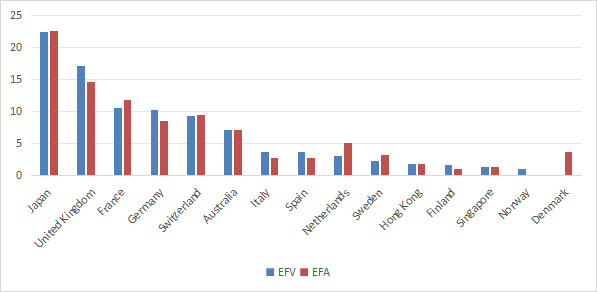
EFV is very heavily represented in the financial sector, with 29.5% of its assets in this sector (nearly 20% in banks). The proportion of industrial goods is 12.7% and other industries are less than 9%. Compared to EFA, EFV is overweighted in finance, energy, utilities, telecommunications and real estate. We are underweight the Industrials, Healthcare, Consumer Discretionary and Technology sectors.
Sectoral analysis as % of asset value (Chart: Author: Data: iShares)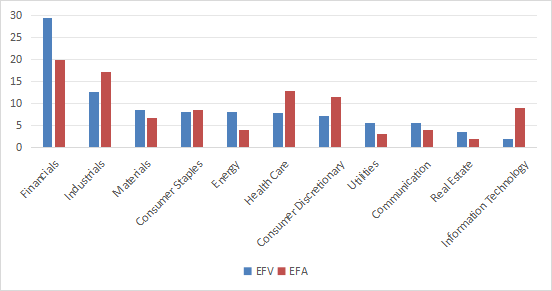
The top 10 holdings listed in the following table represent 18% of assets. The heaviest one is 2.66%, so the risk associated with individual companies is low.
|
name |
sector |
weight% |
exchange |
ticker |
|
shell plc |
energy |
2.66 |
london stock exchange |
shell |
|
Novartis AG |
health care |
2.38 |
SIX Swiss Exchange |
noven |
|
Roche Holding PAR AG |
health care |
2.12 |
SIX Swiss Exchange |
ROG |
|
HSBC Holdings PLC |
finance |
1.95 |
london stock exchange |
HSBA |
|
total energy |
energy |
1.8 |
Nyse Euronext – Paris |
T.T.E. |
|
BHP Group LTD |
ingredient |
1.77 |
Asx – All Markets |
BHP |
|
Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group |
finance |
1.41 |
Tokyo Stock Exchange |
8306 |
|
Allianz |
finance |
1.35 |
jetra |
ALV |
|
Sanofi SA |
health care |
1.3 |
Nyse Euronext – Paris |
SAN |
|
BP PLC |
energy |
1.21 |
london stock exchange |
BP. |
basic
According to the strategy description, EFV is significantly cheaper than the parent index based on the total appreciation ratio reported below. However, the growth rate is only slightly lower.
|
EFV |
EFF |
|
|
Price/Revenue TTM |
11.52 |
15.71 |
|
Price/Book |
1.21 |
1.84 |
|
Price/Sales |
0.99 |
1.47 |
|
Price/Cash Flow |
6.41 |
10.03 |
|
Revenue growth rate (%) |
21.32% |
21.39% |
|
sales growth rate |
7.79% |
8.41% |
|
Cash flow growth rate (%) |
3.67% |
4.88% |
Source: Fidelity.
Performance
Since its inception, EFV has lagged the parent index by 1% in annual returns. It also shows slightly higher risk, as measured by maximum drawdown and standard deviation of monthly returns (volatility).
|
total.returns |
Annual.Returns |
drawdown |
Sharpe ratio |
volatility |
|
|
EFV |
112.78% |
4.09% |
-64.40% |
0.22 |
18.70% |
|
EFF |
154.89% |
5.10% |
-61.04% |
0.28 |
17.52% |
However, EFV has outperformed EFA by 4.5% over the past 12 months.
EFV vs. EFA, 12-month returns (Look for alpha)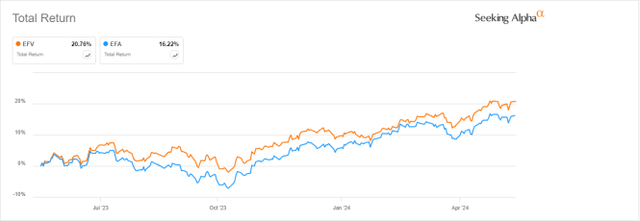
EFVs with returns above 3% can be considered dividend funds in addition to value funds. Between 2013 and 2023, total annual distributions increased 24.7%, from $1.82 to $2.27 per share. This 10-year growth rate is about 32% on a CPI basis, which is lower than the cumulative inflation over the same period. Moreover, there were ups and downs in the distribution, as shown in the chart below.
Distribution history (Look for alpha)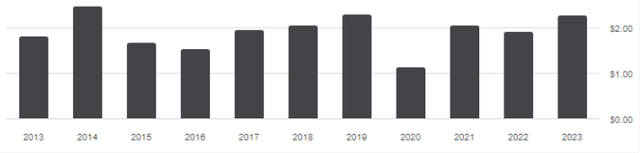
Competitors
The following table compares the characteristics of EFV, which focuses on value stocks and large companies, with three other developed market ETFs excluding the United States.
- Dimensional International Value ETF (DFIV)
- Avantis International Large Cap Value ETF (AVIV)
- Alpha Architect International Quantitative Value ETF (IVAL).
|
EFV |
Aviv |
DFIV |
IVAL |
|
|
Listing date |
August 1, 2005 |
September 29, 2021 |
September 13, 2021 |
December 16, 2014 |
|
cost ratio |
0.34% |
0.25% |
0.27% |
0.39% |
|
operating assets |
$175.6B |
$381.06M |
$7.58 billion |
$154.78M |
|
Average daily trading volume |
$135.25M |
$2.06 million |
$27.27M |
$430.79K |
|
landlord |
474 |
527 |
520 |
57 |
|
top 10 |
17.95% |
17.22% |
16.18% |
21.72% |
|
turnover |
22.00% |
21.00% |
12.00% |
74.00% |
|
Division Yield TTM |
4.03% |
3.39% |
3.42% |
5.42% |
EFV is by far the largest (measured by assets under management) and most liquid (in dollar terms) of these funds. The following chart displays total returns starting from September 30, 2021 to match all listing dates. DFIV performed best and EFV came in second place.
EFV vs. Competitors, September 30, 2021 and Beyond (Look for alpha)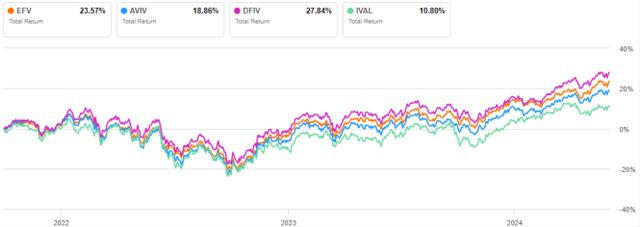
EFV has been roughly the same as DFIV over the past 12 months.
EFV vs Competitors, 12 Month Returns (Look for alpha)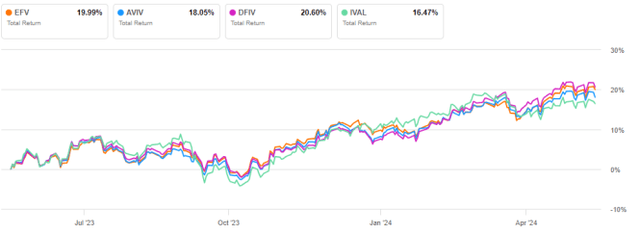
takeout
The iShares MSCI EAFE Value ETF holds approximately 500 stocks with value characteristics listed in developed markets excluding the United States and Canada. EFV is well-diversified by holdings, but is quite heavy in Japan and heavily weighted in the financial sector. EFV has lagged its parent index since 2005, but has outperformed it over the past 12 months. Among value-oriented ETFs that invest in a similar universe of stocks, actively managed fund DFIV has outperformed EFV since September 2021. The main risk factor for EFV is its presence in the banking industry, which is close to 20%.