Ethereum burned $2.5 billion worth of ETH after the merger as supply fell to an 18-month low.

An analysis of Ethereum’s latest financial data for Ultrasound Money reveals a continued shift in its economic model following its historic merger in September 2022.
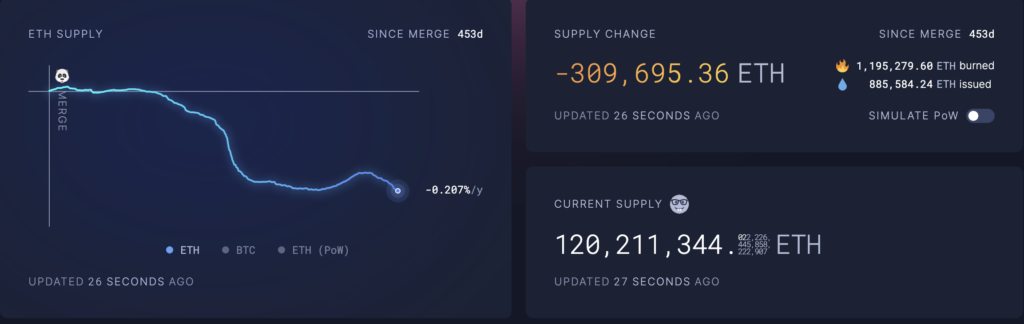
The reduction in Ethereum supply is 309,663 ETH, equivalent to approximately $686.2 million. This decline reflects a deflationary trend in contrast to the previous inflationary nature, when new ETH was constantly being created. The cause of this change can be traced to the burning of 1,195,238 ETH worth approximately $2.65 billion. Permanently removing tokens from circulation plays a significant role in reducing total supply and can improve the scarcity and value of ETH over time. Additionally, despite issuance of 885,581 ETH worth approximately $1.96 billion, Ethereum’s total supply experienced a net decline, showing that the rate of ETH burns continues to outpace the rate of new issuance.
Currently, Ethereum’s total supply is 120,211,380 ETH, the lowest level since the merger, and its market capitalization is approximately $266.39 billion, strengthening its significant position in the cryptocurrency market.
By looking at the ETH burn leaderboard, you can gain more insight by analyzing the key contracts that contributed to ETH burns. Key contributors to this activity include major dApps and services, most notably Uniswap, Tether, and OpenSea in their various iterations. Uniswap’s prominent position suggests high trading volume within the DeFi sector, with $543.8 million burned across the four contracts in the top 10.
Tether’s presence means there has been significant stablecoin trading on the Ethereum network, and OpenSea’s inclusion highlights the persistent nature of NFT trading even in bear markets. This diversity, encompassing DeFi platforms, stablecoins, NFT marketplaces, and layer 2 solutions such as Arbitrum, demonstrates the multifaceted uses of Ethereum.
| Burned ETH | reality | Value (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 84,006.46 | Uniswap universal router | $186,158,315.36 |
| 75,926.77 | Uniswap V2 | $168,253,722.32 |
| 74,739.31 | ETH transfer | $165,622,310.96 |
| 58,030.71 | Uniswap Universal Router 2 | $128,596,053.36 |
| 53,626.72 | rope | $118,836,811.52 |
| 27,441.92 | Uniswap V3 | $60,811,294.72 |
| 26,935.76 | new contract | $59,689,644.16 |
| 23,405.50 | open sea | $51,866,588.00 |
| 22,891.92 | decision | $50,728,494.72 |
| 22,201.66 | metamask | $49,198,878.56 |
Source: ultrasound.money
The total burn amount of the top 10 contracts is $1,039,762,113.68 worth of ETH, which is just under half of the total burn amount since the merger.
Ethereum’s shift to a deflationary model could continue to attract investors seeking a store of value, especially when contrasted with inflation-prone fiat currencies. Increasing activity in decentralized exchanges and DeFi applications signals a strong trend toward decentralized finance.
Interestingly, under the current Proof-of-Stake (PoS) model, the Ethereum network has burned an average of 1.83 ETH/minute since the merge. However, since the burn mechanism was implemented as part of the EIP-1559 upgrade in August 2021, the average burn rate is almost double to 3.09 ETH/min. However, since proof-of-work mining was abolished, the amount of supply issued has decreased sharply, and the overall supply has been steadily decreasing.
If Ethereum had remained in PoW mode, supply would have reached a whopping 124,941,176 ETH, about 4.7 million ETH more than current levels. In theory, at the current price of $2,228, Ethereum’s market cap would be $12 billion higher than its current $266 billion. Importantly, with increased supply, this is only academic due to the nature of supply/demand market dynamics.
Going forward, these dynamics could impact Ethereum’s trajectory in a variety of ways. Continued deflationary trends could lead to increased demand and potentially higher ETH prices. This is possible under the assumption that demand remains steady or increasing during a bear market. However, it is important to consider that external factors such as market volatility and regulatory changes or macroeconomic trends, particularly the ongoing efforts of the US SEC to classify PoS tokens as securities, may have a significant impact on these dynamics.
In summary, Ethereum’s post-merger statistics indicate a notable move towards a deflationary framework, highlighted by high network usage and the potential for value appreciation due to declining supply, especially in the DeFi and NFT sectors. However, these trends warrant continued analysis and understanding of macroeconomic factors to fully understand their long-term impact and sustainability.