How Bitcoin Can Improve Water Abundance in Water-Scarce Countries

The claim that “Bitcoin runs on fossil fuels” is increasingly becoming increasingly common in the face of new data from Bloomberg Intelligence showing that the network is actually the most sustainable energy-supporting industry on the planet, with 53% of its energy coming from sustainable sources. It’s falling apart.
In response to this news, a new attack vector emerged: “Bitcoin uses too much water.” Obviously, if Bitcoin uses fossil fuels as an energy source, that’s bad, but if it uses hydropower, it’s also bad. This is the same double bind that 17th century witch hunters used to determine if a woman was a witch. water. If she can swim she is a witch. Execute her her. “If she falls into the water and cannot swim, it is proof that she is not a witch.”
Of course, that’s an absurd claim you can make against any electricity user you want to criticize. As for the method used by study author de Vries to measure water use per transaction, Cambridge has already debunked energy use per transaction and further stated that resource use per transaction “is not a meaningful metric.”
This hasn’t stopped many journalists from starting to research. As I wade through this symphony of off-the-wall journalism, I became curious: “What is the real story of Bitcoin and water?”
So I decided to do some research on the other side of the ledger. Can Bitcoin Help Water Security?
Where do real water shortages exist?
First, let’s find out which country is suffering the most from water shortage. A quick Google search revealed that “of the 17 most water-scarce countries in the world, 12 live in the Middle East or North Africa.”

in sati
Intrigued, I asked more details about how these countries were coping with this water shortage.
It turned out that the situation was very serious.
- 60% of these countries are experiencing “severe water stress.”
- Scientists expect the situation to worsen as the climate warms.
- Over the past 30 years, precipitation has decreased by 16.7%.
- Many of these countries currently use more water than they produce.
-Source: CNBC, Could the Middle East be running out of water?
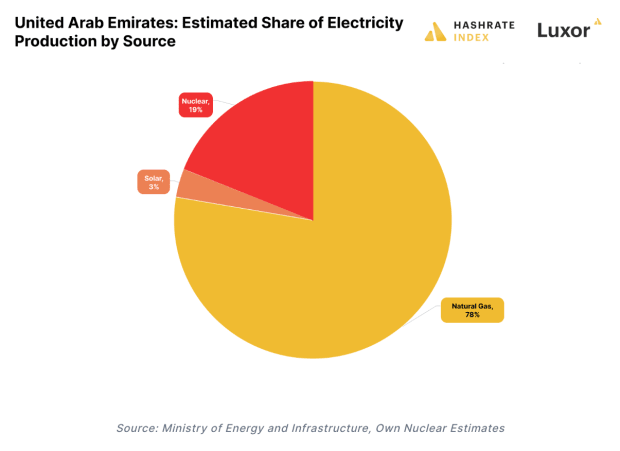
Rich countries like the UAE use desalination to solve this problem. However, desalination is expensive and energy-intensive. It also has many environmental challenges, not least of which is the fact that 78% of the UAE’s energy comes from fossil fuels (natural gas).
According to The National News, desalination plants are essential if the world is to have enough water to drink.
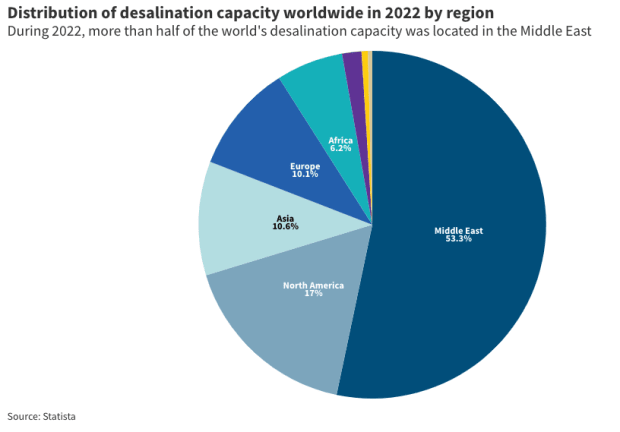
Some estimates predict there will be a 40% gap between water supply and demand by 2030. Global dependence on desalination is increasing, with 53% of global desalination already occurring in the Middle East.
Efforts are increasingly being made to use renewable energy to power desalination plants, but these projects will take time. New technologies must be developed and new solar power facilities must be built.
“We are working on hybridization (desalination systems) with renewable energy such as wind, wave and solar,” said Dr. Muhammad Wakil Shahzad, a senior lecturer at the University of Northumbria, UK, who developed the patented desalination system. “We have several prototypes in our lab,” he said.
These solar farms could be used to provide an alternative to burning natural gas to power desalination plants. Crucially, the UAE is planning large-scale solar power facilities in its vast, sunny desert. The country’s largest solar project will be 5GW, making it one of the largest in the world. Until 2030.
Luxor’s Jaran Mellerud said these solar installations “will undoubtedly produce huge amounts of power on a regular basis.”
How Bitcoin Helps Water Scarcity #1: Accelerating Deployment of Renewable Power Desalination
Absorbing excess solar power and becoming a buyer are two areas where Bitcoin mining can help provide a solution to water scarcity.
According to Mellerud, “Bitcoin miners, who are location-agnostic and uninterruptible electricity consumers, can set up operations directly on these solar farms to recover wasted electricity and generate revenue.” (Source: HashrateIndex). A recent study from Cornell University confirmed that Bitcoin mining can increase the profitability of solar power operators, allowing them to scale their solar power businesses faster.
Bitcoin mining could help the UAE transition to renewable desalination by accelerating the construction of new solar energy capacity. This means the UAE can achieve its water security goals without jeopardizing its emissions reduction targets.
How Bitcoin Mining Helps Water Scarcity #2: Increasing Desalination Efficiency
As CNBC reports, desalination is energy intensive. Therefore, increased efficiency in operating costs means that water can be desalinated with the same operating costs. That is why UAE water management, whether through desalination or underground aquifers, is constantly striving to increase operational efficiency.
This is where an exciting and pioneering Bitcoin mining project is already underway. Marathon Digital Holdings recently partnered with Zero Two.
Typically, heat is used directly for desalination. However, Zero Two and Marathon realized that almost 100% of the energy used by Bitcoin mining equipment is converted to thermal energy. If that heat can be recycled, it can be reused. And that recycled heat is now being used for desalination. The only difference is that the desalination plant is making money from Bitcoin mining. In other words, your water per dollar ratio improves. Being able to desalinate more water at the same net cost is an incredible achievement. Marathon CEO Fred Thiel explains. For desalination plants, Bitcoin mining “allows energy production to continue to operate profitably, using heat to create desalinated water.”
summary:
The place in the world where water is most scarce, and where water is becoming more scarce, is the Middle East.
For these countries, desalination is an ideal solution. This is why 53% of all desalination currently takes place in the Middle East. However, desalination is carbon-intensive and energy-intensive. Bitcoin mining helps solve both problems. First, by becoming a buyer of energy that would otherwise have been wasted, it helps to increase the profitability of solar deployments in the Middle East, thereby increasing their carbon intensity. Second, it increases the profitability of desalination plants by allowing them to generate Bitcoin and use ASICS’ waste heat for desalination. This means the plant can profitably desalinate more water.
In short, far from being a source of concern about global water use, Bitcoin is helping the world’s most water-scarce places profitably achieve water security without jeopardizing their emissions targets. This is something that no other technology can currently do.
This is a guest post by Daniel Batten. The opinions expressed are solely personal and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.


