Investor’s Guide to Layer 2 – Bitcoin Market Journal

Key Takeaways
- Layer-2 (L2) protocols are an auxiliary framework that builds on top of existing, more secure blockchain networks to make them more accessible.
- This increases transaction efficiency by offloading processes from the main chain and is very similar to TradFi’s SWIFT messaging network.
- Investors can invest in the tokens of these Layer-2 projects, holding or staking them to identify long-term winners.
index
- What is Layer 2?
- Why is Layer-2 important?
- Layer-2 and SWIFT
- Upper Layer 2 Blockchain
- What is Layer 2 blockchain used for?
- Investor Outlook on Layer-2
- Investor Implications
We often think of blockchain as a single technology, but it is a layer of multiple technologies working together.
Layers are not ideal. As you start to reach higher levels, in most cases the base chain compensates for the lack of scalability. They are hacks.
In this guide, we explain what Layer 2 is and how investors can think about the ultimate winner of the Layer 2 race so that they can invest in today’s tokens that are most likely to win in the long term.
What is Layer 2?
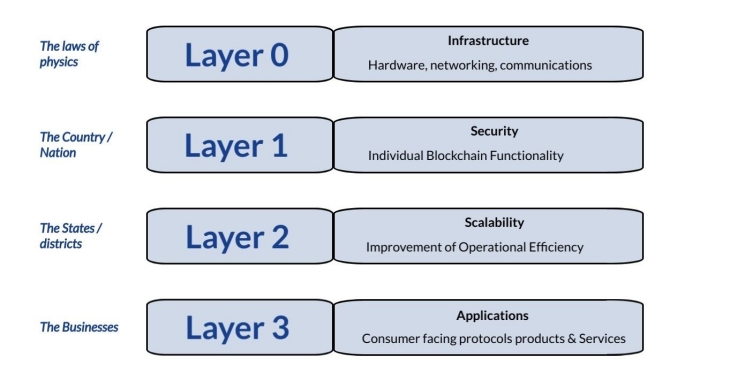
Blockchain technology consists of four layers.
- Layer-0 (L0) It consists of the Internet and the hardware needed to connect and communicate over a network.
- Layer-1 (L1) Refers to major blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, that focus on recording transactions, forming consensus, and maintaining security.
- Layer-2 (L2) We focus on scaling these solutions.
- Layer-3 (L3) Focus on application hosting to drive adoption.
Layer 2 means: A set of technology solutions built on top of Layer 1 to reduce bottlenecks (i.e. to help the underlying blockchain run faster and cheaper).
It uses L1 blockchain for security and data availability and generally consists of two parts: data packets and protocol layer. Where data packets represent encoded and decoded bits of information, the protocol layer focuses on transferring data from one network segment to another.
While Layer 1 is the foundation of decentralized finance, Layer 2 blockchain solutions are built to improve scalability and compatibility with third-party applications.
For example, Ethereum is a popular Layer-1 but does not scale well. Therefore, layer 2 solutions like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base are built to make Ethereum run faster and cheaper.
Why is Layer-2 important?
As the number of blockchain users increases, scalability issues also increase. Layer 2 blockchains solve these problems by offloading transactions from the main chain and processing them separately. Layer 2 networks typically provide:
- low fees: Layer 2 protocols bundle off-chain transactions into a single Layer 1 transaction, reducing data load on the mainnet while maintaining the benefits of security and decentralization.
- more utilities: Layer 2 projects can improve user experience while focusing on scope and real-world usability by allowing for higher transaction throughput.
Imagine having to send money abroad in the early 1900s. To purchase bank drafts accepted abroad, you must use gold or silver coins. You can mail a bank draft to the person you want to send money to.
When SWIFT was invented in 1973, the money transfer process was slow, dependent on individual couriers, and prone to delays and losses.
SWIFT stands for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication and is the primary messaging network for international payments. To this day, SWIFT remains the default standard for international money transfers and works by sending important information about the transaction from one bank to another, including the sender’s name, the recipient, the transaction amount, and the exchange rate.
Layer 2 blockchains operate similarly to SWIFT. They build and improve existing infrastructure to ease the remittance process. SWIFT represents a scenario where one layer 2 blockchain becomes the default solution for scalability. We will all utilize a single messaging system to interact with major networks.
That said, the key point is also what differentiates Layer-2 from SWIFT. Layer 2 solutions are decentralized, meaning transactions are not overseen by a central authority. SWIFT is a centralized system managed by a consortium of banks.
Due to the involvement of multiple intermediaries and TradFi’s rigorous processes, SWIFT transactions take longer to settle than blockchain transactions.
Upper Layer 2 Blockchain

Each type of Layer 2 solves a different problem. Depending on your blockchain or user needs, one Layer-2 solution may be better than another.
- status channel: State channels are a blockchain second layer solution that allows participants to conduct unlimited private transactions off-chain. This is ideal for situations that require frequent two-way transactions, such as in-game microtransactions and live stream donations.
- Optimistic Rollup: To process transactions faster, layer 2 solutions can aggregate multiple off-chain transactions into one, assume them to be valid by default, and only execute calculations if there is a dispute. This is how optimistic rollups work and are suitable for DApp and DeFi platforms.
- ZK roll up: Zero-knowledge rollups create a more secure blockchain than optimistic rollups by compressing transaction data, validating off-chain transactions, and transmitting this information to the main chain. Similar to optimistic rollups, this type of Layer-2 is suitable for dapps and DeFi platforms and offers improved privacy and efficiency.
- plasma: Plasma chains, which provide the highest level of security among layer 2 types, are linked by smart contracts that allow the main chain to guide child chains, creating a series of child chains as auxiliary chains that support the main blockchain through verification. do.
- sidechain: A sidechain is an independent blockchain that runs in parallel with the main blockchain. It is suitable for applications that require customizable features and independent governance of the main chain while solving tasks at the base layer.
What is Layer 2 blockchain used for?
Layer 2 protocols extend the functionality and scalability of central blockchain networks, making it much easier for these projects to support (and disrupt) the industry. Some of these industries include:
DeFi
Improving trading speed is crucial in DeFi, especially in trading where timely execution can determine the difference between profit and loss. For example, Loopring uses ZK-Rollups to facilitate high-speed trading and transfers for traders.
Dapp
Batch processing and improved interoperability allow dapps to process more transactions across multiple applications. Polygon is a layer 2 scaling solution that allows dapps to operate on a variety of blockchain platforms without compromising performance.
micropayment
Layer 2 solutions lower average transaction fees, making micropayments available at a much lower cost to users. Gaming ecosystems and live streamers can use this feature for monetization purposes or pay-as-you-go models.
Investor Outlook on Layer-2
The history of technology may provide some clues about how Layer-2 competition will unfold.
Typically, with new technologies, there is an explosion of new competitors (search engines, social media sites, etc.) that gradually coalesce into several scenarios.
- monopoly: There is one dominant solution that holds most of the market share because other solutions are too inconvenient to use. (Think Google search.)
In this scenario, one large Layer-2 will dominate each underlying Layer-1 blockchain. (And there may only be one underlying layer 1 blockchain.) In this scenario, the current winners would be Ethereum (ETH) and Polygon (MATIC), so investors would adjust their bets accordingly.
- oligopoly: There are two or three dominant solutions that effectively crowd out the rest of the market (e.g. Apple and Windows or iPhone and Android).
In this scenario, several Layer-2s may survive, each offering significantly different developer benefits. For investors, the layer 1 bet may still be Ethereum (ETH), but as for the layer 2 bet, it is still too early to tell.
- disruptive technology: Sometimes the underlying technology is transformative or disruptive. (Disk drives, CD-ROMs, digital music stores, etc.).
Layer 2 cannot win in this scenario because Layer 1 finds ways to increase scalability without layers. In this case, Ethereum (ETH) would be the primary long-term investment.
For the time being, Layer-2 solutions are adding value. However, a winner-takes-all or winner-takes-all outcome is likely. Of course, unless layer 1 is significantly improved, layer 2 becomes obsolete.
Investor Implications
For investors, Layer-2 solutions present both opportunities and challenges.
Smart investors should investigate the unique features of each Layer 2 solution, but more importantly, their market traction. Are you attracting real users – not just investors hoping for an airdrop, but real users using it and real developers developing it?
This is the initial stage of Layer-2. In the future, they will either be consolidated or discarded. A high quality Layer-1 like Ethereum is still likely to be a safer investment for most investors.
Subscribe to Bitcoin Market Journal to follow every step of blockchain investing.



