S&P Global warns about impact of spot Ethereum ETF on staking concentration

In a recent analysis, S&P Global Ratings highlighted that the possible approval of a spot Ethereum (ETH) exchange-traded fund (ETF) with a staking scheme could amplify concentration risks within the Ethereum network.
According to reports, the SEC may approve the ETH ETF as early as May. However, the entry of ETFs could significantly shake up Ethereum’s balance of validator power, presenting new challenges and opportunities as financial heavyweights compete for a stake in this emerging sector.
The SEC has until May 23 to decide on VanEck’s application, and could rule on other ETH ETF applications by that deadline.
concentration risk
Ark Invest and Franklin Templeton’s Spot Ethereum ETF proposal aims to generate additional income by staking ETH. However, S&P Global analysts wrote that if staking-enabled ETFs receive sufficiently high inflows, this could impact the participation rate in the Ethereum verification network.
According to the report, Lido currently accounts for less than a third of staked ETH and is the largest Ethereum validator. However, the report casts doubt on the likelihood of these ETFs opting for a decentralized staking protocol like Lido.
Instead, a preference for institutional cryptocurrency custodians seems more likely, suggesting that validator concentration may be affected differently depending on the issuer’s diversification strategy.
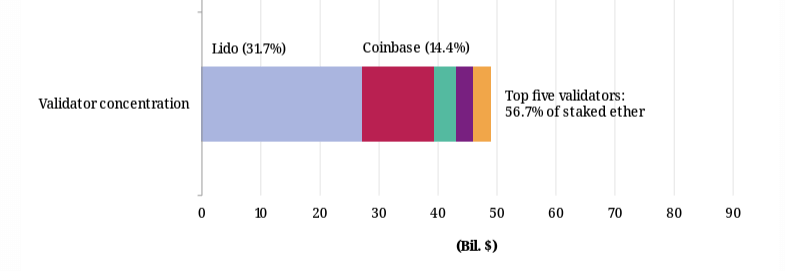
The report also highlighted that Coinbase, which acts as custodian for some funds, could pose concentration risks if it acquires new ETH on behalf of U.S. ETFs.
The exchange currently accounts for around 15% of staked ETH, making it the second-largest validator overall. It also serves as custodian for three of the four largest Ethereum ETFs outside the United States.
The report said these issues are important because relying on a single entity or software client can lead to the risk of verifier outages and attacks. This called for and highlighted the importance of greater monitoring of concentration risks.
The emergence of new digital asset custodians could provide a path for ETF issuers to distribute their holdings more broadly, which could also mitigate concentration risk.
JP Morgan expresses concern.
S&P Global’s report echoes concerns recently raised by JP Morgan in a similar analysis of a spot Ethereum ETF. The lender’s report also concluded that the dominance of Lido and Coinbase poses significant concentration risk to the ecosystem.
JP Morgan argued that a concentrated number of validators could become a single point of failure, jeopardizing the stability and security of the network. This centralization also presents a lucrative target for malicious attacks, from hacking attempts to organized network disruptions.
JPMorgan analysts also warned of possible collusion between key validators. An oligopoly of validators can manipulate the network’s governance and operating parameters to its advantage at the expense of Ethereum’s broad user base.
This can manifest itself as censorship of transactions, preferential treatment of certain operations, and preemption, which can undermine trust in Ethereum’s fairness and transparency.
Ensuring that Ethereum remains a strong, secure, and decentralized platform requires a concerted effort to mitigate concentration risk and create an environment where no single validator or group of validators can exercise disproportionate power.



